Step 1:

DNA is extracted from the nucleus of cells in tissue, blood, or fluids. (it takes longer to test for DNA in hair, bone, or mitochondria DNA). Next, the DNA is "washed" with chemicals to remove unwanted cell material.
Step 2:
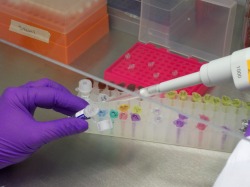
Tests are ran to determine the amount of recovered DNA present. (Targeted amounts is approximately 1 nanogram [1 billionth of a gram]). If there aren't enough quantities of DNA that's recovered, then step one might have to be repeated.
Step 3:
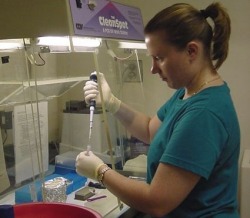
Chemicals are added to allow specific fragments of DNA to reproduce millions of times. 13 specific DNA locations are targeted for examination through a machine that cycles heating and cooling steps.
Step 4:

A machine called a genetic analyzer will record images of DNA segments as it moves through a small tube. When the results come in, they will appear as spikes or peaks. Then, a computer generates the results.
